Technology
Unlocking the Future of Cloud with SDCS Technology

In the rapidly advancing landscape of technology, SDCS (Software-Defined Cloud Services) is emerging as a groundbreaking concept that holds the potential to transform how businesses manage, deploy, and scale their IT infrastructure. This article delves into SDC’S technology, its significance, its components, and the role it plays in enabling businesses to harness the power of the cloud efficiently.
1. Introduction to SDCS Technology
What is SDCS?
SDCS stands for Software-Defined Cloud Services. At its core, SDC’S is a set of technologies that abstract, virtualize, and automate key elements of cloud infrastructure to provide a more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution for businesses. SDC’S builds on the principles of Software-Defined Infrastructure (SDI), which decouples hardware from software, allowing for a more agile approach to managing cloud resources.
In traditional cloud models, the management of compute, storage, and networking resources is closely tied to the underlying physical hardware. This can limit flexibility, increase costs, and complicate scaling operations. SDCS takes a more holistic approach by decoupling these resources from physical hardware through software, enabling more dynamic management and greater control over the cloud environment.
The Evolution of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has evolved significantly since its inception. Initially, cloud services were limited to Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), providing virtual machines (VMs) and basic computing resources. As demand grew for more flexible, scalable, and automated cloud environments, the industry introduced Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS), extending the cloud’s capabilities.
However, as businesses began to leverage cloud solutions more extensively, it became clear that traditional cloud services still had limitations in terms of agility and operational efficiency. In response, SDCS was developed as a means to address these gaps. By shifting from hardware-defined to software-defined models, SDC’S allows organizations to scale and adjust their cloud infrastructure rapidly while keeping costs under control.
The Need for SDCS in Modern IT Infrastructure
Modern IT infrastructures are growing more complex, with organizations seeking to optimize performance, reduce operational overhead, and stay competitive. Traditional cloud solutions often struggle to meet these needs due to their dependence on rigid, hardware-based configurations.
SDCS technology fills this gap by providing an abstraction layer that decouples hardware from software. This enables faster provisioning, automated scaling, and better resource management. In the age of multi-cloud strategies and digital transformation, SDC’S ensures that businesses can maximize their IT investments and meet the increasing demand for cloud-based services.
2. Key Components of SDCS Technology
To understand SDC’S technology more thoroughly, it’s essential to break down its key components, which work together to create a flexible and efficient cloud environment.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is a crucial component of SDCS technology. It involves the virtualization of network infrastructure, allowing network management to be controlled by software rather than relying on traditional hardware-based devices like routers and switches. With SDN, network configuration and management can be automated, improving both agility and scalability.
SDN allows for dynamic traffic routing, bandwidth allocation, and network segmentation. This makes it possible to build and maintain complex networks without the need for manual configuration of each individual device, which is both time-consuming and error-prone.
Software-Defined Storage (SDS)
Software-Defined Storage (SDS) refers to the abstraction of storage resources through software rather than relying on specific storage hardware. SDS makes it easier to manage storage resources across different platforms, enabling businesses to scale their storage needs without being tied to specific hardware solutions.
SDS technologies enable automated storage provisioning, improved storage efficiency, and better data protection. By abstracting storage resources, SDS simplifies data management, ensuring that businesses can store and retrieve information in a manner that is cost-effective and responsive to their needs.
Software-Defined Compute (SDC)
Software-Defined Compute (SDC) refers to the abstraction and management of compute resources (servers and processing power) through software. SDC allows businesses to optimize compute resources dynamically based on demand. Instead of relying on physical servers or hardware to perform specific tasks, SDC ensures that compute resources are provisioned automatically and adjusted based on real-time needs.
This flexibility allows businesses to deploy applications more efficiently, improve resource utilization, and scale compute power with minimal manual intervention.
Integration and Automation in SDCS
One of the core features of SDCS technology is its integration with automation tools. These tools enable the automated provisioning, monitoring, and management of resources across the cloud infrastructure. Automation reduces the need for manual configuration, improves operational efficiency, and ensures that resources are allocated based on the actual demand.
Integration with cloud management platforms and orchestration tools further enhances the capabilities of SDCS, allowing for seamless coordination across different layers of the cloud infrastructure, including compute, storage, and networking.
3. How SDCS Works
Virtualization and Abstraction Layers
The core principle behind SDCS is virtualization. Virtualization enables the decoupling of physical hardware from the software that runs on it. In a typical cloud infrastructure, hardware resources such as compute, storage, and networking are all tightly coupled with their respective physical devices. SDC’S changes this by introducing layers of abstraction, which means that cloud resources are not tied to any specific hardware but instead managed through software.
This abstraction allows businesses to manage their cloud infrastructure in a more flexible and efficient manner. Resources can be allocated dynamically, and workloads can be moved between different systems or even across different cloud environments with minimal disruption.
Centralized Control
SDC’S systems typically feature centralized control planes that allow administrators to manage resources across a distributed network of cloud nodes. Through a unified interface, businesses can monitor, configure, and scale their cloud resources according to their needs. Centralized control also facilitates automation, ensuring that cloud resources are allocated and decommissioned according to predefined policies.
Benefits of a Software-Defined Approach
The software-defined approach to cloud infrastructure brings several significant benefits:
- Increased Flexibility: SDCS enables businesses to adjust their resources based on changing demands, whether it’s scaling up for peak loads or scaling down during off-peak times.
- Cost Efficiency: By optimizing resource allocation and automating tasks, SDCS helps organizations reduce operational costs, minimize hardware expenditures, and avoid over-provisioning.
- Better Resource Utilization: SDC’S ensures that cloud resources are used optimally, reducing wastage and improving efficiency.
4. The Benefits of SDCS Technology
Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability
One of the primary advantages of SDCS technology is its ability to provide enhanced flexibility and scalability. By decoupling cloud resources from the underlying hardware, SDCS enables businesses to scale up or down quickly and easily, responding to fluctuations in demand without incurring significant costs. This agility allows companies to meet customer needs more effectively, without the constraints of traditional hardware-based infrastructure.
Cost Efficiency
SDC’S is designed to be cost-effective by reducing the reliance on physical hardware, allowing businesses to provision resources more efficiently. Through the use of virtualization, businesses can maximize resource utilization and avoid overprovisioning, which often leads to wasted capacity. Additionally, SDCS makes it possible to use cheaper commodity hardware, further lowering infrastructure costs.
Improved Performance and Reliability
With SDCS, businesses can benefit from improved performance and reliability. Automated resource management and centralized control enable businesses to maintain high levels of performance without the risk of hardware failure. SDC’S can intelligently allocate resources based on current demand, ensuring that applications perform optimally even during peak usage times.
Simplified Management and Automation
SDCS simplifies the management of cloud resources by providing a centralized platform that automates the provisioning, monitoring, and maintenance of resources. Automation helps reduce the risk of human error, accelerates response times, and allows IT teams to focus on more strategic tasks. By automating repetitive processes, SDC’S also improves operational efficiency.
5. Applications of SDCS Technology
Cloud Service Providers (CSPs)
Cloud service providers are the primary beneficiaries of SDC’S technology. With SDCS, CSPs can offer more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions to their customers. By decoupling infrastructure resources from hardware, CSPs can more efficiently manage their data centers, deploy new services, and offer multi-tenant environments with improved performance.
Enterprise IT Infrastructure
Enterprises are increasingly adopting SDCS to manage their internal IT infrastructures. By leveraging SDCS, organizations can build and scale their private cloud environments more effectively. The ability to automate resource management, improve security, and ensure compliance with industry regulations makes SDC’S an ideal solution for businesses with complex IT needs.
Data Centers and Network Optimization
SDCS can be used to optimize data center operations by automating resource allocation, improving power efficiency, and reducing physical space requirements. Data centers can also benefit from the flexibility to quickly scale resources based on demand and optimize networking operations with SDN technologies.
6. Challenges in Implementing SDCS
While SDCS offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges. Some of the key obstacles organizations may face include:
- Security and Compliance Concerns: The abstract nature of SDC’S raises concerns around data security and compliance. Businesses must ensure that security policies are effectively implemented and that regulatory requirements are met.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Integrating SDCS with legacy systems and hardware can be complex and costly. Organizations may need to invest in additional tools or platforms to bridge the gap between modern SDCS technologies and older infrastructure.
- Vendor Lock-in Risks: Adopting SDCS solutions from a particular vendor can sometimes result in vendor lock-in. Organizations must carefully evaluate the potential risks of being tied to a single provider, especially in a multi-cloud environment.
7. The Future of SDCS
As cloud computing continues to evolve, the future of SDCS looks promising. Key trends that will shape the future of SDCS include:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can further automate resource management, predict demand spikes, and optimize resource allocation in real time.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Environments: As businesses increasingly adopt multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, SDCS will play a key role in providing seamless management across different cloud environments.
- Evolving Use Cases and Industry Adoption: As SDCS technology matures, new use cases and industries will adopt this technology, ranging from edge computing to IoT.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, SDCS technology represents the future of cloud computing, offering businesses the flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency needed to thrive in a digital-first world. By abstracting and automating cloud resources, SDCS enables organizations to manage their IT infrastructure more effectively while reducing costs and improving performance. As the technology continues to evolve, SDCS will become an essential part of modern IT strategies, paving the way for more agile and efficient cloud environments.
Read: Understanding SteamRip: A Comprehensive Guide
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is SDCS technology, and how does it differ from traditional cloud computing?
Answer: SDCS (Software-Defined Cloud Services) is a technology that abstracts, virtualizes, and automates cloud resources, enabling greater flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. Unlike traditional cloud computing, which often relies on fixed hardware configurations, SDCS allows businesses to manage cloud resources through software.
2. What are the main components of SDCS?
Answer: The main components of SDCS include Software-Defined Networking (SDN), Software-Defined Storage (SDS), and Software-Defined Compute (SDC), all of which are managed and orchestrated through software to create a more flexible and scalable cloud environment.
3. What are the advantages of SDCS technology?
Answer: SDCS offers several benefits, including enhanced flexibility, cost efficiency, improved performance, simplified management, and automation of cloud resources. It enables businesses to scale infrastructure dynamically based on demand.
4. How does SDCS improve cloud resource management?
Answer: SDCS improves cloud resource management by automating the provisioning, monitoring, and allocation of resources. This reduces manual intervention, minimizes errors, and ensures efficient resource utilization across cloud environments.
5. What are the challenges of implementing SDCS?
Answer: Challenges of implementing SDCS include security and compliance concerns, integration with legacy systems, and the risk of vendor lock-in. Organizations must address these challenges through careful planning and evaluation.
6. What does the future of SDCS look like?
Answer: The future of SDCS involves further integration with AI and machine learning for automation, support for multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, and the expansion of use cases across industries such as edge computing and IoT. As the technology matures, its adoption will continue to grow, transforming cloud computing.
Technology
Coax: An In-depth Guide to Coaxial Cables and Their Applications
Coaxial cables, commonly referred to as “coax,” are an essential component of modern communication systems. From delivering cable television signals to enabling high-speed internet, coaxial cables have revolutionized how data and signals are transmitted. This article dives deep into the world of coaxial cables, covering their structure, functionality, uses, benefits, limitations, and the future of this technology. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of why coax cables remain relevant despite advancements in fiber-optic and wireless technologies.
Understanding Coaxial Cables
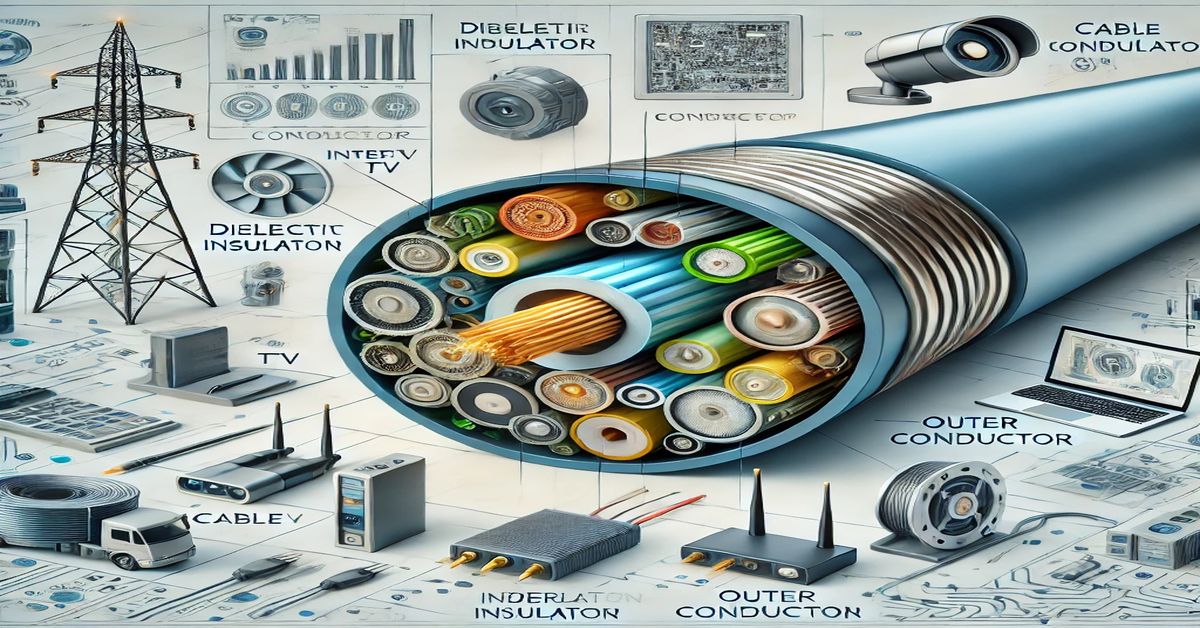
Coax cables are specialized cables designed for transmitting high-frequency electrical signals with minimal loss. Their unique design helps shield the transmitted signals from electromagnetic interference (EMI), ensuring clear and reliable communication. The term “coax” is derived from the cable’s geometry, where the central conductor and the outer conductive layer share a common axis.
Structure of Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables have a distinct multi-layered structure, optimized for signal transmission:
- Inner Conductor:
- The core component of the cable, typically made of copper or copper-clad steel.
- Responsible for carrying the electrical signal.
- Dielectric Insulator:
- Surrounds the inner conductor and separates it from the outer conductor.
- Made of materials like polyethylene or Teflon, which ensure minimal signal loss.
- Outer Conductor (Shield):
- A braided or solid metallic layer, often made of aluminum or copper.
- Protects the inner conductor from external electromagnetic interference.
- Outer Jacket:
- The final protective layer, made of PVC or other durable plastics.
- Shields the cable from physical damage, moisture, and environmental factors.
How Coaxial Cables Work
Coax cables work by transmitting signals through the inner conductor, while the outer conductor acts as a shield against interference. The dielectric insulator maintains a uniform distance between the two conductors, ensuring consistent signal quality. This design allows coaxial cables to carry high-frequency signals over long distances with minimal degradation.
Types of Coaxial Cables
There are various types of coax cables, each designed for specific applications. Some of the most common types include:
- RG-6:
- Widely used for cable television, satellite, and internet services.
- Offers low signal loss and superior shielding.
- RG-59:
- Common in CCTV systems and short-distance video applications.
- Less effective for high-frequency signals over long distances.
- RG-11:
- Used for long-distance signal transmission.
- Features thicker conductors and better shielding.
- Hardline Coaxial Cables:
- Designed for high-power applications, such as radio transmitters and cellular networks.
- Equipped with rigid outer conductors for enhanced durability.
- Tri-axial (Triax) Cables:
- Include an additional layer of shielding.
- Used in professional video applications to reduce interference.
- Semi-Rigid Coaxial Cables:
- Feature a solid metal outer jacket.
- Ideal for military and aerospace applications.
Applications of Coaxial Cables
Coax cables are versatile and find use across various industries. Some of their most prominent applications include:
1. Television Broadcasting
Coaxial cables have been the backbone of cable television systems for decades. They efficiently deliver high-quality audio and video signals from broadcasting stations to homes, ensuring minimal loss and interference.
2. Internet Connectivity
Cable internet providers rely on coaxial cables to transmit data. Coaxial cables support broadband connections and enable high-speed internet access, making them integral to modern communication networks.
3. CCTV and Security Systems
In surveillance systems, coaxial cables are used to connect cameras to recording devices and monitors. Their ability to transmit high-resolution video signals over long distances makes them a preferred choice for CCTV installations.
4. Telecommunications
Coaxial cables play a critical role in telephone networks and other telecommunications systems, enabling reliable voice and data transmission.
5. Military and Aerospace
Due to their durability and ability to shield against interference, coaxial cables are used in military and aerospace applications for radar systems, navigation equipment, and secure communication lines.
6. Medical Equipment
In the medical field, coaxial cables are used in imaging systems like MRI and CT scanners, where signal integrity is crucial.
7. Amateur Radio and Broadcasting
Radio enthusiasts and broadcasters use coaxial cables to connect antennas, transmitters, and receivers, ensuring optimal signal performance.
Advantages of Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables offer several benefits that contribute to their widespread use:
- High Bandwidth:
- Capable of transmitting large amounts of data at high speeds.
- Signal Integrity:
- Provides excellent shielding against EMI, ensuring clear and reliable signal transmission.
- Durability:
- Resistant to environmental factors, physical damage, and wear and tear.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- More affordable than fiber-optic cables for certain applications.
- Ease of Installation:
- Simple to install and maintain, with readily available connectors and tools.
- Compatibility:
- Supports a wide range of devices and systems, from televisions to internet modems.
Limitations of Coaxial Cables
Despite their advantages, coaxial cables have some limitations:
- Signal Loss:
- Over long distances, coaxial cables can experience signal attenuation, requiring signal boosters or amplifiers.
- Bulkiness:
- Thicker and less flexible than some modern alternatives like twisted-pair cables.
- Limited Scalability:
- May struggle to meet the demands of high-speed data transmission compared to fiber optics.
- Vulnerability to Moisture:
- If not properly sealed, coaxial cables can be damaged by moisture ingress, leading to signal degradation.
- Interference in Poor Quality Cables:
- Low-quality coaxial cables may not provide adequate shielding, resulting in EMI issues.
Coaxial Cables vs. Other Transmission Media
Coaxial vs. Fiber Optic
- Speed: Fiber-optic cables offer significantly higher speeds than coaxial cables.
- Distance: Fiber optics can transmit signals over much longer distances without degradation.
- Cost: Coaxial cables are more cost-effective for shorter distances and less demanding applications.
Coaxial vs. Twisted Pair
- Interference: Coaxial cables provide better shielding against EMI.
- Cost: Twisted-pair cables are generally cheaper and more flexible for short-distance applications.
- Bandwidth: Coaxial cables support higher bandwidth compared to standard twisted-pair cables.
The Future of Coaxial Cables
While technologies like fiber optics and wireless communication are gaining traction, coaxial cables remain relevant for several reasons:
- Infrastructure Investment:
- Existing coaxial networks are well-established, making them cost-effective for continued use.
- Hybrid Systems:
- Many modern systems use a combination of coaxial and fiber-optic cables, leveraging the strengths of both.
- Advancements in Coaxial Technology:
- Innovations like DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification) have improved the speed and efficiency of coaxial networks, enabling gigabit internet speeds.
- Niche Applications:
- Coaxial cables excel in applications requiring high durability and EMI resistance, ensuring their continued use in specialized fields.
Conclusion
Coaxial cables have stood the test of time, proving to be a reliable and versatile medium for signal transmission. Their unique design, combined with advancements in technology, ensures their relevance in a rapidly evolving communication landscape. From television broadcasting to high-speed internet and beyond, coaxial cables continue to play a pivotal role in connecting the world. As hybrid systems and technological innovations emerge, coaxial cables are likely to remain an integral part of modern communication networks for years to come.
FAQs
1. What is a coaxial cable used for?
Coaxial cables are used for transmitting high-frequency electrical signals, primarily in applications like cable television, internet connectivity, CCTV systems, telecommunications, and professional broadcasting.
2. How does a coaxial cable differ from a fiber-optic cable?
Coaxial cables transmit electrical signals, while fiber-optic cables use light signals. Fiber optics offer higher speeds and longer transmission distances but are more expensive than coaxial cables.
3. Can coaxial cables support high-speed internet?
Yes, coaxial cables can support high-speed internet, especially with technologies like DOCSIS, which enable gigabit speeds over coaxial networks.
4. Are coaxial cables durable?
Coaxial cables are highly durable and resistant to environmental factors, physical damage, and wear, making them suitable for various demanding applications.
5. What are the limitations of coaxial cables?
Coaxial cables can experience signal loss over long distances, are bulkier than alternatives like twisted-pair cables, and may not scale well for ultra-high-speed data transmission compared to fiber optics.
6. Is coaxial cable still relevant in the age of fiber optics?
Yes, coaxial cables remain relevant due to their cost-effectiveness, widespread infrastructure, and ability to complement fiber-optic networks in hybrid systems.
Technology
Openo: Understanding the Platform, Its Features, and Impact

Openo, a groundbreaking platform in the field of technology and innovation, has been capturing the attention of industries, developers, and users alike. This comprehensive article will delve into the core concepts of Openo, its unique features, advantages, and the impact it is creating across various sectors. We will explore its architecture, applications, and potential future, providing an informative overview for enthusiasts and professionals.
What is Openo?
Openo is an open-source software platform designed to streamline and simplify complex technological processes. It aims to integrate, automate, and manage various components of software and hardware systems. As a modular and scalable platform, Openo’s supports diverse use cases ranging from enterprise-level automation to smaller-scale software development projects.
The essence of Openo lies in its adaptability and user-centric design. By providing a robust and flexible framework, it enables developers to build solutions tailored to their specific needs while fostering collaboration and innovation within the community.
Core Features of Openo
Openo distinguishes itself through a range of innovative features that make it a versatile tool for various applications:
1. Open-Source Framework
As an open-source platform, Openo’s allows developers to access its source code, enabling customization and collaboration. This transparency fosters trust and empowers the community to contribute to its evolution.
2. Modular Architecture
Openo’s is built on a modular architecture, allowing users to add or remove components based on their requirements. This ensures flexibility and scalability, making it suitable for projects of all sizes.
3. Integration Capabilities
The platform seamlessly integrates with existing tools and systems, ensuring compatibility and smooth operation. This reduces the need for overhauling existing infrastructure, saving time and resources.
4. Automation
Openo excels in automating repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency and productivity. From workflow management to resource allocation, its automation capabilities streamline operations.
5. Community Support
A vibrant community of developers and enthusiasts backs Openo’s. This support network provides resources, forums, and updates, ensuring users stay informed and connected.
6. Scalability
The platform is designed to scale with the growth of a business or project. Its robust architecture accommodates increasing complexity without compromising performance.
7. Security Features
Openo prioritizes security, incorporating encryption, authentication protocols, and regular updates to protect data and systems from potential threats.
Applications of Openo
Openo’s versatility has led to its adoption across various industries and use cases. Below are some prominent applications:
1. Enterprise Solutions
Businesses leverage Openo’s to manage and automate complex workflows. It is particularly beneficial for resource management, data analysis, and operational efficiency.
2. Software Development
Openo simplifies the software development process by providing tools for version control, testing, and deployment. Its modularity supports agile methodologies and DevOps practices.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
In IoT ecosystems, Openo’s enables the integration and management of connected devices. It ensures seamless communication between hardware components and software applications.
4. Cloud Computing
Openo is widely used in cloud environments to orchestrate services, manage resources, and ensure optimal performance. Its scalability aligns well with the dynamic nature of cloud computing.
5. Education and Research
Educational institutions and researchers use Openo’s to develop prototypes, conduct experiments, and create innovative solutions. Its accessibility makes it an ideal choice for academic environments.
Benefits of Using Openo
Openo offers a plethora of advantages that contribute to its growing popularity:
1. Cost-Effectiveness
Being open-source, Openo’s eliminates licensing costs, making it a budget-friendly option for individuals and organizations.
2. Customization
Users can tailor the platform to suit their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and functionality.
3. Enhanced Productivity
By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining workflows, Openo’s boosts productivity and reduces manual effort.
4. Innovation
Openo’s collaborative ecosystem fosters innovation by encouraging knowledge sharing and community contributions.
5. Future-Ready
Its adaptability ensures that Openo’s can evolve with technological advancements, keeping users ahead of the curve.
Technical Architecture of Openo
Openo’s technical architecture is a cornerstone of its functionality and reliability. Here is an overview of its key components:
1. Core Engine
The core engine is the heart of Openo’s, responsible for executing commands, managing processes, and maintaining system stability.
2. API Layer
Openo’s API layer facilitates integration with third-party tools and services. It provides developers with the flexibility to extend its functionality.
3. User Interface
The platform features an intuitive user interface that simplifies navigation and operation, ensuring accessibility for users of all technical levels.
4. Data Management
Openo’s includes robust data management capabilities, ensuring efficient storage, retrieval, and processing of information.
5. Security Modules
Its security modules safeguard sensitive data and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its numerous advantages, Openo’s is not without challenges:
1. Learning Curve
New users may find the platform’s extensive features overwhelming, requiring time and effort to master.
2. Dependency on Community Support
While the community is a strength, reliance on it for updates and support can be a limitation in critical situations.
3. Compatibility Issues
Integrating Openo’s with older or proprietary systems may pose challenges due to compatibility constraints.
The Future of Openo
The future of Openo is promising, with potential advancements in the following areas:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
Incorporating AI could enhance Openo’s capabilities, enabling smarter automation and predictive analytics.
2. Broader Industry Adoption
As awareness grows, more industries are likely to adopt Openo’s, expanding its application scope.
3. Enhanced User Experience
Continuous updates and improvements will likely make Openo more user-friendly and accessible.
4. Greater Collaboration
The community-driven approach will lead to innovative features and solutions, further solidifying Openo’s position in the market.
Openo is a powerful platform that embodies the spirit of innovation and collaboration. Its open-source nature, coupled with its flexibility and scalability, makes it a valuable tool across diverse sectors. By understanding its features, applications, and potential, users can leverage Openo to drive efficiency, creativity, and growth.
Read: Darktide Chat Not Working: Troubleshooting and Solutions
FAQs
1. What is Openo used for?
Openo is used for automating workflows, managing resources, and integrating software and hardware systems across various industries, including enterprise solutions, IoT, and cloud computing.
2. Is Openo free to use?
Yes, Openo is an open-source platform, making it free to use. Users can access its source code and customize it as needed.
3. What are the key features of Openo?
Key features include a modular architecture, integration capabilities, automation, scalability, and robust security measures.
4. Can Openo integrate with existing systems?
Yes, Openo supports seamless integration with various tools and systems, enhancing compatibility and functionality.
5. Who can benefit from Openo?
Developers, businesses, educational institutions, and researchers can benefit from Openo by streamlining processes and fostering innovation.
6. What challenges does Openo face?
Challenges include a steep learning curve for new users, dependency on community support, and potential compatibility issues with legacy systems.
Technology
Darktide Chat Not Working: Troubleshooting and Solutions

“Warhammer 40,000: Darktide” is one of the most anticipated multiplayer games of recent years. Developed by Fatshark, the game promises an engaging and chaotic co-op experience set in the Warhammer 40k universe. One of the crucial components of any multiplayer game is communication, and in darktide chat not working, that communication typically happens through an in-game chat system. Whether players are discussing strategy, warning others about upcoming threats, or just having fun, the chat function is essential for enhancing the multiplayer experience.
However, like many online games, players may sometimes encounter issues with the chat system not working properly. This can be frustrating, especially when teamwork is vital for success in the game. Whether it’s issues with voice chat, text chat, or other forms of communication, troubleshooting Darktide’s chat problems can often be straightforward once you understand where the issue lies.
In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the common reasons why the chat may not be working in Warhammer 40,000: Darktide, along with various troubleshooting methods and solutions to resolve these issues. By the end of this guide, you will be well-equipped to solve the problem and get back to playing with your team without communication barriers.
Why is Darktide Chat Not Working?
There are several reasons why the chat feature in Darktide might not be functioning as expected. These reasons can range from basic software issues to network connectivity problems. Below are some of the most common causes for chat malfunctions in Darktide.
1. Server Issues
One of the most common causes of chat not working in any online game is server-related problems. If Darktide’s servers are experiencing downtime or heavy load due to a recent update or a sudden surge in player numbers, chat services may be affected. Players often encounter delays, disconnections, or complete outages when server-side issues occur. This can affect voice and text chat functionality.
To check if server issues are the culprit, visit Darktide’s official social media pages, forums, or the developer’s website. Many developers provide status updates or maintenance notices if there’s an issue on their end.
2. Chat Settings and Permissions
Sometimes, players may unknowingly adjust their in-game settings, which can affect the chat system. Darktide has several different types of chat: team chat, global chat, and sometimes voice chat. If one of these options is disabled or muted, players may not see or hear messages from others. Additionally, if you have unintentionally set the chat to “whispers” or private mode, you may only be able to communicate with specific players.
It’s worth checking your chat settings and ensuring that everything is configured properly for the type of communication you want. If the game has any built-in chat restrictions, such as blocking specific keywords or filtering content, it may also prevent you from receiving certain messages.
3. Network and Connectivity Problems
Network issues can disrupt the overall performance of online games, including the chat feature. If your internet connection is unstable or you’re experiencing packet loss or high latency, it could cause delays in text or voice chat messages. Additionally, firewall or antivirus software might block certain ports or connections needed for the chat system to function correctly.
Testing your network speed and connection, or temporarily disabling the firewall/antivirus (if safe to do so), may help you determine if your internet is the issue. Also, consider switching to a wired connection if you’re using Wi-Fi, as wired connections typically offer more stable and reliable performance.
4. Corrupted Game Files
Over time, game files can become corrupted due to various factors, such as incomplete installations, errors during updates, or hardware issues. Corrupted files may cause various game functions, including the chat system, to behave unpredictably.
To verify if corrupted game files are causing the issue, you can use Steam’s built-in “Verify Integrity of Game Files” feature. This tool will check if any of the game’s files are missing or damaged and automatically repair them.
5. Outdated Drivers or Software
If your system’s graphics or audio drivers are out of date, it could cause issues with the game’s audio and chat functionality. In some cases, outdated drivers can result in a loss of voice chat or prevent you from hearing other players. Likewise, outdated versions of the game itself may not be compatible with certain in-game features.
To fix this, ensure that both your game and system drivers are up to date. Updating your drivers for audio devices, graphics cards, and network adapters can help resolve performance issues that might be affecting chat.
6. Chat Server Overload
Chat servers, like any other server system in an online multiplayer game, can become overloaded during peak hours. This can lead to chat delays or outright failures. Overload can occur when too many players are trying to use the chat system at once, causing messages to be delayed or lost entirely. Server optimization can mitigate these issues, but during periods of heavy load, there may be performance degradation.
7. Game-Specific Bugs or Glitches
No game is entirely free from bugs or glitches, and Darktide is no exception. Sometimes, chat problems arise due to specific game bugs, such as issues with how the chat system is integrated with the rest of the game. If the chat is failing sporadically, or certain types of chat (e.g., voice chat, team chat) are not functioning, it could be a bug in the game’s code.
In these cases, it’s helpful to check for official updates or patches from the developer. Game developers typically address these issues through updates and bug fixes.
Troubleshooting Solutions
Now that we’ve discussed the potential causes of chat issues in Darktide, let’s look at some troubleshooting solutions to fix the problem.
1. Check Server Status
The first step when encountering chat problems is to check whether there is an ongoing server issue. Visit the official Warhammer 40,000: Darktide website or follow the developer’s social media accounts for updates on server status. If servers are down or under maintenance, chat issues may be temporary, and you can wait until the problem is resolved.
2. Verify Chat Settings
Ensure that your chat settings are properly configured. Go to the settings menu in Darktide and double-check the chat options. Make sure that both text and voice chat are enabled. Additionally, check if any filters or restrictions are in place that may limit your ability to send or receive messages.
3. Restart the Game or Computer
If the chat isn’t working, a simple restart of the game or your computer can sometimes resolve minor software glitches. Closing unnecessary background applications may also help free up system resources, which can improve the game’s performance.
4. Check Your Network Connection
Test your internet connection by running a speed test. If your connection is slow or unreliable, this could be affecting your chat functionality. Try restarting your router or connecting to a different network. If you’re on Wi-Fi, consider switching to a wired connection to improve stability.
If you suspect that your firewall or antivirus is blocking chat features, temporarily disable them (ensure your computer’s security is not compromised) to see if it resolves the issue.
5. Verify Game Files
To rule out corrupted files, use Steam’s built-in tool to verify the integrity of your game files. This process will scan the game for missing or damaged files and automatically replace them, which can resolve issues caused by corrupted data.
To verify game files:
- Open Steam and go to your Library.
- Right-click on Darktide and select “Properties.”
- Click on the “Local Files” tab and select “Verify Integrity of Game Files.”
- Steam will check for any missing or corrupted files and replace them as needed.
6. Update Drivers and Software
Ensure that your system drivers are up to date. Focus on updating your audio drivers, graphics card drivers, and network adapter drivers. Keeping your operating system and game updated is also important to ensure compatibility and avoid bugs that could interfere with the chat feature.
Conclusion
The chat function in Darktide is crucial for coordinating with your team, strategizing, and enjoying the full multiplayer experience. However, issues with chat can occur for a variety of reasons, from server issues to network problems or corrupted game files. By following the troubleshooting steps outlined above, players should be able to diagnose and resolve most common chat problems.
If the issue persists, it may be a result of a bug or other technical issue that needs to be addressed by the developers. In such cases, players should report the problem to Fatshark for further investigation. With proper attention, most chat-related problems can be fixed, allowing you to communicate effectively and enjoy the intense cooperative action that Darktide has to offer.
FAQs
- Why is the chat not working in Darktide?
- Chat issues can be caused by server problems, incorrect settings, network issues, corrupted game files, or outdated software/drivers.
- How do I enable the chat in Darktide?
- Go to the settings menu and ensure both text and voice chat are enabled. Check if any filters are in place.
- How can I check if Darktide’s servers are down?
- Visit the official Darktide website or follow Fatshark’s social media accounts for server status updates and maintenance announcements.
- Why is my voice chat not working in Darktide?
- Voice chat may not work due to settings issues, network problems, or conflicts with your microphone. Ensure voice chat is enabled in settings and that your microphone is working.
- How do I verify if my Darktide game files are corrupted?
- Use Steam’s “Verify Integrity of Game Files” option found in the game’s properties under the “Local Files” tab.
- What should I do if I continue to experience chat problems in Darktide?
- If basic troubleshooting doesn’t work, check for software updates, report the issue to the developers, or visit relevant forums for advice from the community.
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoFSI Blog: Your Gateway to Financial, Strategic, & Industry Insights
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoJeinz Macias: A Comprehensive Insight into the Legacy & Influence
-

 Games6 days ago
Games6 days agoUnderstanding SteamRip: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days ago5StarsStocks.com Dividend Stocks: Building Wealth with Dividend Investments
-

 Technology5 days ago
Technology5 days agoEditor benjamin tech guru keezy.co: Innovating with Technology
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoYuppow: Revolutionizing Work, Life, and Digital Innovation
-

 Entertainment6 days ago
Entertainment6 days agoDopeBox: Online Entertainment Cutting-Edge Streaming Solutions
-

 Entertainment6 days ago
Entertainment6 days agoTara Tainton: Background, Career, and Legacy